- Blog
PC Case Fan Types & Characteristics | Q&A
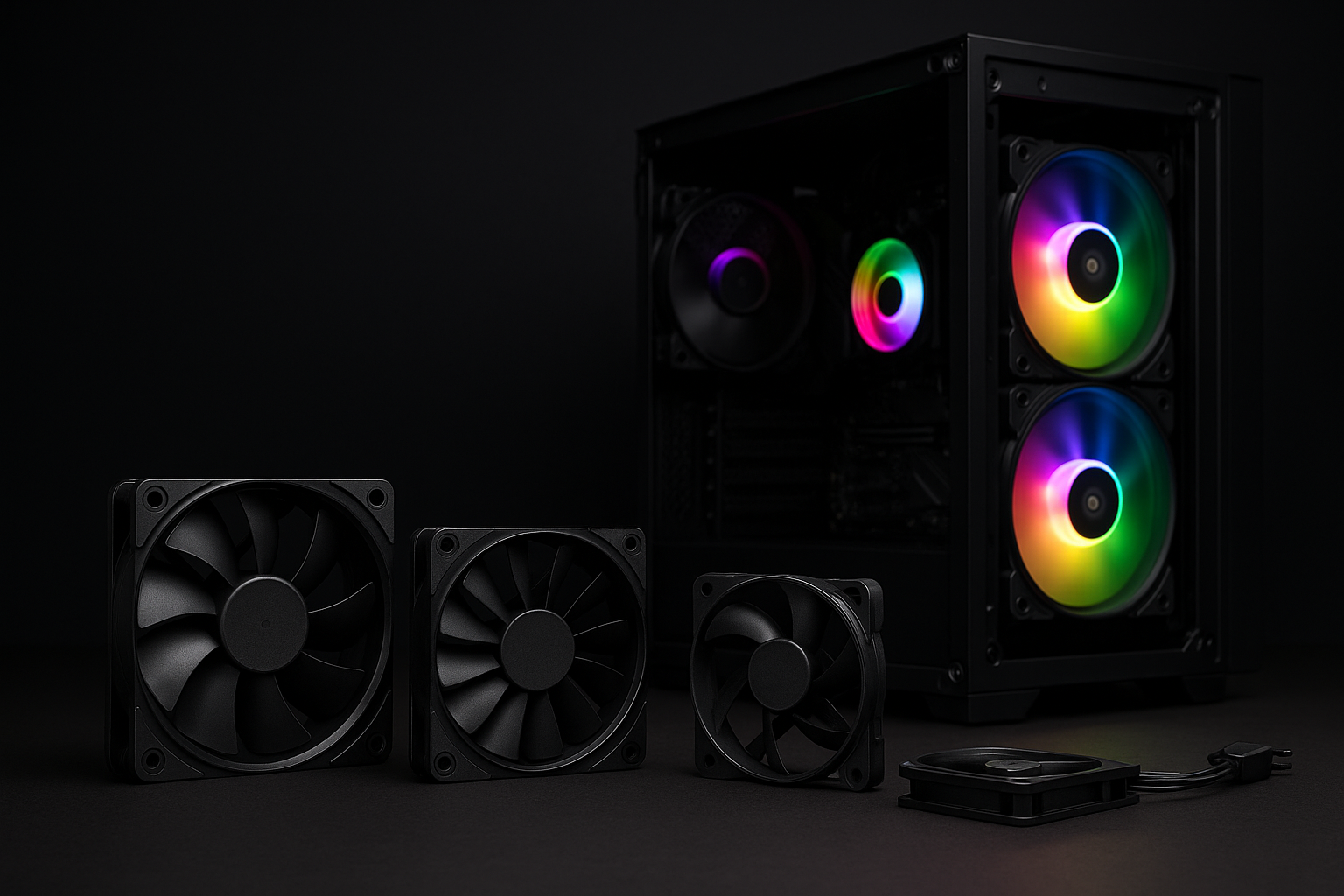

Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is an Airflow fan?
Airflow-oriented fans have wider, flatter blades and can run at higher RPMs. They’re designed to maximize air volume (CFM), ideal for open intake/exhaust spots (front/side) to rapidly exchange case air and lower overall temps. The key idea is circulation, not fighting resistance (as often noted in be quiet!’s docs).
Use cases: front intake, top intake (large openings/no filter), standard rear exhaust.
Buying tips: prioritize CFM and low-RPM noise; pair with open/high-flow panels for best results.

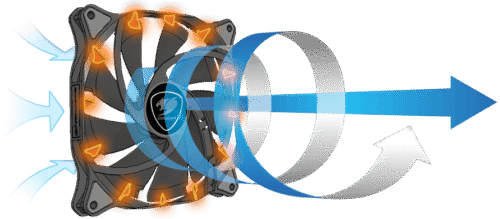
What is a Static Pressure fan?
Static-pressure fans use steeper blade angles and tighter sealing to push air through resistance (radiators, thick filters, tight meshes). They’re common on radiators or dense fin stacks and are recommended in such scenarios.
Use cases: AIO/DIY radiators (top/front), front panels with thick filters or grilles, dense tower heatsinks.
Buying tips: prioritize static pressure (mmH₂O) and mid/low-RPM efficiency; sealed frames help reduce leakage.

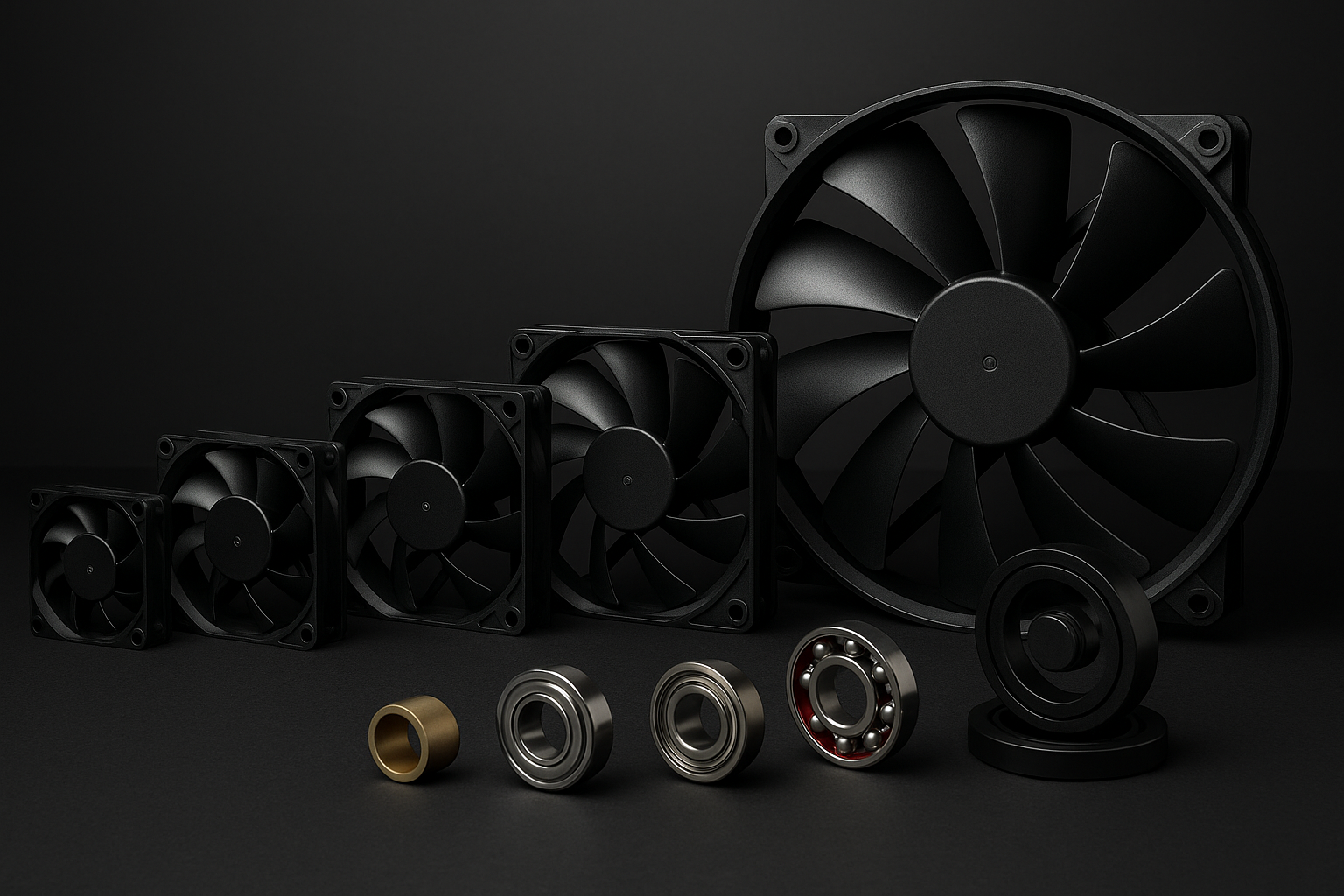
What is a Slim fan?
Slim fans are 15–17 mm thick (about 7–10 mm thinner than standard 25 mm). They’re built for tight spaces such as ITX cases or positions close to radiators/heatsinks. While airflow/pressure is usually lower, well-designed slim models still offer usable cooling—popular in HTPCs and SFF builds.
Use cases: shallow top/bottom mounts, GPU/PSU interference zones, ITX/SFF.
Buying tips: confirm thickness and screw pattern; check noise curve vs usable static pressure.

What is an ARGB fan?
ARGB fans feature addressable lighting (each LED can change color individually). Blades/frames often include light guides, combining cooling with aesthetics. Functionally they’re standard fans, but can sync effects via motherboard or controller—great for visual builds.
Use cases: glass-side cases, front/side visible positions, system-wide lighting sync.
Buying tips: don’t mix 5 V 3-pin ARGB with 12 V 4-pin RGB; ensure adequate lighting power/Hub capacity.

What is a MagLev (magnetic-levitation) fan?
MagLev bearings suspend the rotor with magnetic force, minimizing contact and friction. Result: very low noise, better heat tolerance, and long lifespan. In practice (e.g., ROG Strix XF120), these fans balance low noise with solid CFM and pressure; Sunon specs commonly cite lifetimes around 50,000 hours at room temp.
Use cases: long duty cycles, silence-focused rigs, radiators or general case use.
Buying tips: check bearing type (MagLev), rated acoustics, and warranty; expect higher prices than typical FDB.

What is a Reverse-Blade fan?
Reverse-blade fans curve opposite to traditional designs, giving a clean front view (no visible struts)—popular for “showcase” fronts. Testing generally shows similar airflow/pressure to the matched standard model (e.g., ~73 CFM, ~2.66 mmH₂O for 120 mm class), with negligible noise differences at like RPMs.
Use cases: front display positions where aesthetics matter most.
Buying tips: mind airflow direction and rotation; verify compatibility with filters/panels.

What are flow straighteners and guide vanes?
Some fans/frames add guide vanes or flow straighteners to smooth inlet/outlet flow, reduce vortices and wind noise, and direct air more precisely into heatsinks or vents—improving efficiency and acoustics. Many PSUs/fans also market “patented” guide frames for aero-noise reduction.
Use cases: radiator/tower alignment, directional ducting, longer throw paths.
Buying tips: ensure the guide geometry aligns with fin stacks/vent patterns to avoid leakage.
What is a modular daisy-chain fan?
Modular (daisy-chain) fans physically link multiple units, sharing PWM/ARGB signals and power—dramatically reducing cables and simplifying sync. Lian Li’s UNI FAN series, for example, uses interlocking connectors for tidy wiring and centralized control, perfect for triple-fan front/top rows.
Use cases: multi-fan front/top banks, builds prioritizing cable cleanliness and synchronized lighting.
Buying tips: confirm the brand’s hub/cable ecosystem, motherboard headers, SATA power capacity, and max chain length.